Innovating with Immersive Reality
Projects in this theme aim to develop novel applications of virtual reality and augmented reality to serve the unmet needs in industry verticals such as healthcare, education and entertainment.
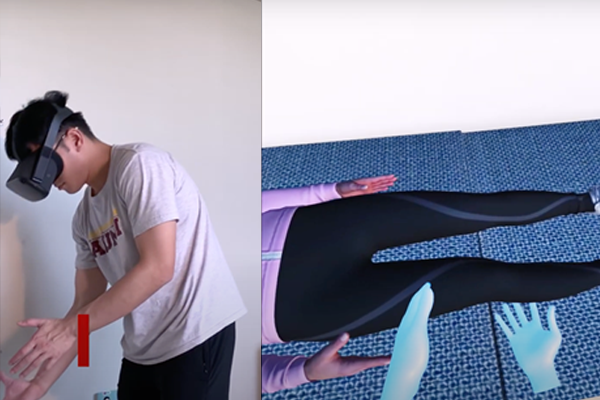
This project develops a novel AI conversational agent and hands tracking to allow orthopedic residents to use natural language to interact with the virtual patient and bare hands to execute physical examination. A dialog model was built from scratch using Rasa X, RASA Core and Microsoft Azure, and trained to handle the unpredictability of patient-doctor conversations.
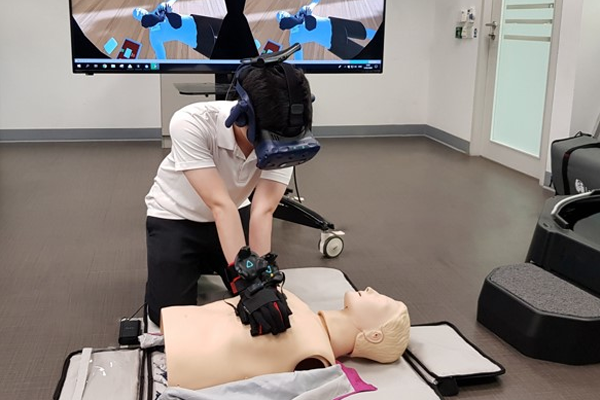
Basic Cardiac Life Support training is essential for all medical staff and actively promoted to the general public. However, the training is manpower intensive and has limited availability to the public. We have developed a novel VR training solution using VR head mounted display, hand gloves and Resusci Anne Manikin, that could be used out-of-the-box without medical personnel intervention. User training data are logged and feedback is provided in real time. This project is developed in collaboration with Sengkang General Hospital and is funded by iHIS Research Innovation Enterprise Partnership grant.
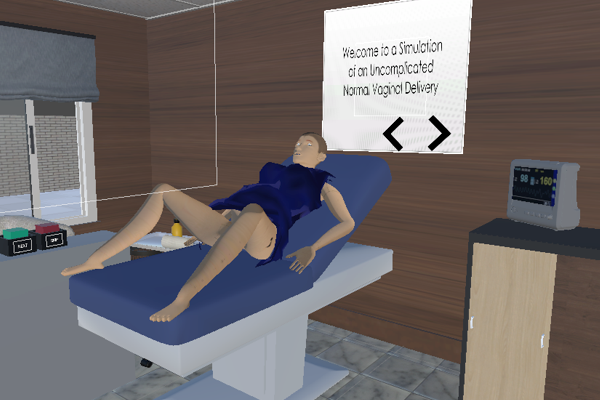
This project aims to develop a birth delivery simulator targeted towards undergraduate medical students whom often do not have the opportunity to be in the delivery suite to perform hands-on procedures. They have to make do with a manikin for training, which is not realistic and does not train well for complications. This project intends to provide a realistic training toolkit through virtual reality with haptics for birthing simulations, from normal delivery to complication. This project is developed in collaboration with Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, NUH and NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine.
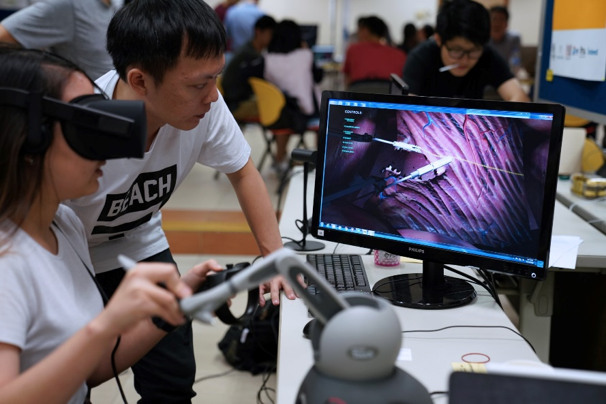
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) is becoming more popular due to its various benefits compared to conventional surgery. One of the ways to carry out MIS is using the da Vinci surgical system. However, this system has a steep learning curve and is not accessible. We have developed a virtual simulator incorporating VR system and the Geomagic Touch haptic device. We focused the training on soft tissue cutting which is an essential skill for robotic surgeons. This project is developed in collaboration with NUH Gynaecologic Robot Assisted Cancer & Endoscopic Surgery programme and NUS School of Computing.
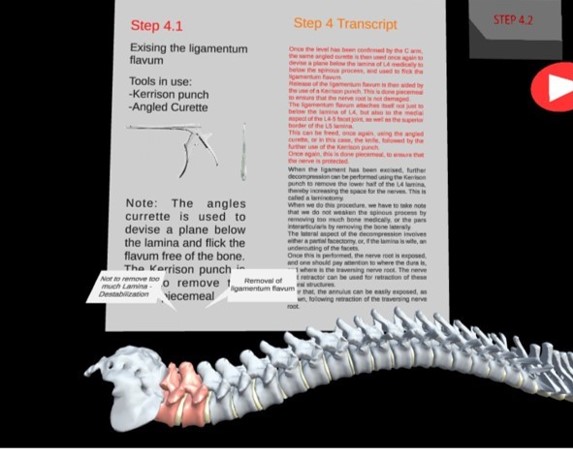
Resident doctors at orthopedic surgery are seeking more training opportunity outside of operating room. With high-fidelity interactive stereoscopic recordings of spinal surgical procedures, we are able to transport the resident into the shoes of the operating surgeon. We do this by utilizing state of the art stereo cameras, and the Oculus Quest, with its built in positional tracking systems. Resident doctor can also review the lecture notes and 3D spine model in VR. This project is developed in collaboration with the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery at NUH and NPLASTY.
Museum Alive project explores innovative technology to transform museum experience, provide additional contexts to the paintings and promote dialogue and interaction among visitors. What experiences did the painter go through in his or her life? What was the political situation at the time they were painting it? These, and many other contexts, add depth to a painting. An Augmented Reality app was developed to track paintings in real time. Additional contexts are overlaid on demand. New context hotspots could also be added to the cloud database through the app, promoting an open dialogue among visitors.
Learning martial art movement requires thorough practice and correction, especially for novice. In this Wushu project, we hypothesised that movement can be learned more effectively if feedback on the movement can be provided to the learner in a direct way using a virtual ghost model of the instructor. The instructor’s moves are pre-recorded using wearable VR trackers. The movements are played in segments with selectable playback speed in a form of ghost model to the trainees. The VR system also provide real time feedback on the accuracy of the body movement and total score at the end of each exercise.
Fire is a hazard that can happen anywhere and everyone should be prepared for it. However, hands-on training is costly in terms of manpower and resources and is limited due to the potential hazards of an actual fire. For the general population, infrequent hands-on practices and non-hands-on training materials limit their preparedness.The advantages of the Virtual Reality based training tool include reducing manpower and resource needs, not having to set up a real fire and increasing the accessibility to a minimum standard of hands-on practice.
This project explores the usage of virtual reality in aircraft maintenance. Integration of virtual reality in aircraft maintenance training helps to reduce the training costs while ensuring a safe environment for trainees. The developed prototype combines visuals, haptics, movement and spatial sound cues in a head gear to create a realistic virtual environment for training.